This infographic from PixlParade examines how much 46 different countries put towards healthcare and military spending in 2018, per capita.
Head to Head: Healthcare versus Military
Data for government and compulsory healthcare spending comes from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Note that these figures do not include spending through private insurance or out-of-pocket expenses. Meanwhile, the data for military spending comes from the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI). Note: There are minor discrepancies in comparing table data to original sources due to recent estimate updates. Figures for Brazil, South Africa, China, Indonesia, and India come from the World Bank (2017).
The Top 10 Healthcare Spenders
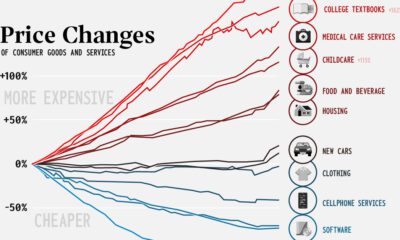
The U.S. leads the world in government healthcare spending at $9,008 per capita – over 1.5 times that of Norway, the next-highest country examined. While per-capita government spending on healthcare in the U.S. is the highest in the world, this has not necessarily brought about better outcomes (such as longer life expectancy) compared to other developed nations. It’s also worth mentioning that the above figures do not cover all healthcare costs incurred by citizens, as they do not account for private insurance spending or out-of-pocket expenses. According to OECD data, these additional costs tend to be the highest in places like Switzerland and the United States.
The Top 10 Military Spenders
Israel has the highest rate of military spending per capita, and has the distinction of being the only country on this list to invest more in defense than in healthcare. Although the United States comes in second place here as well, in absolute terms, the U.S. puts more money into military expenditures than many other countries combined, at almost $700 billion per year. on After a year of casualties, structural devastation, and innumerable headlines, the conflict drags on. Many report the impacts to the economy, social demographics, and international relationships, but how do science and academia fair in the throes of war? Within the actions and responses of the conflict, we take a look at how six key scenarios globally shape science.
War’s Material Impacts to Science
1. Russia Invades Ukraine
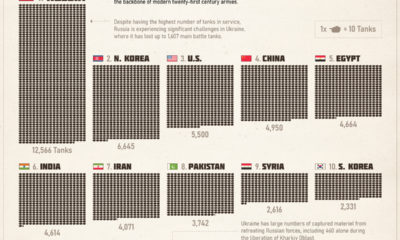
The assault to research infrastructure in Ukraine is devastating. Approximately 27% of buildings are damaged or destroyed. The country’s leading scientific research centers, like the Kharkiv Institute of Physics and Technology, or the world’s largest decameter-wavelength radio telescope, are in ruins. While the majority of research centers remain standing, many are not operating. Amidst rolling blackouts and disruptions, a dramatic decrease in research funds (as large as 50%) has cut back scientific activity in the country. Rebuilding efforts are underway, but the extent to which it will return to its former capacity remains to be seen.
2. Ukraine Fights Back
As research funds have been redirected to the military, and scientists, too, have pivoted in a similar way. Martial law and general mobilization have enlisted male researchers, especially those with military experience and those within the 18-60 age range. Women were exempt until July 2022. Those with degrees in chemistry, biology, and telecommunications were required to enter the military registry. For both men and women researchers alike, these requirements meant staying in the country for the remainder of the year. Extensions for mobilization have subsided as of February 19th, 2023.
Social Impacts of War to Science
3. Western Leaders Exclude Russia
One year ago, scientists and institutions around the world immediately launched into protest against Russia’s escalation:
The European Commission agreed to cease payments to Russian participants and to not renew contract agreements for Horizon Europe The $300-million, MIT-led Skoltech program was dissolved one day after the war began, with no foreseeable restart in the future Various governments and research councils in the European Union froze collaborations and discouraged working with Russian institutions The European Organization for Nuclear Research, CERN, barred all Russian observers and will dismiss almost 8% of its workers—about 1,000 Russian scientists—hen contracts expire later this year
These condemnations, and more, remain in effect today and are emboldened by what has come to be known as a “scientific boycott”. Journal publishers around the world imposed some of their own sanctions on Russian institutions and scientists in light of this boycott. These range from prohibiting Russian manuscript submissions (Elsevier’s Journal of Molecular Structure) to scrubbing journal indices of Russian papers and authors.
4. Russia Dissociates from the West
As a response to the sanctions imposed on the Russian economy, Russia ceases to sell natural gas to most of Europe. Institutions are reassessing their usage and dependence on Russian energy, but alternatives are not yet affordable. The German Electron Synchrotron (DESY) in Hamburg, home to the world’s most powerful X-ray laser, is struggling with rising electricity costs. CERN, for instance, has already cut its data collection for the year by two weeks in order to save money. This makes it difficult for pre-war projects to continue collaborating with Russia. As a result, there are questions about how withdrawals may be affecting Russian science, too. For now, that remains relatively unknown, though some have guesses. Young scientists, many barred from attending international conferences and meetings, may seek employment or opportunity elsewhere to develop their careers. Some speculate a “brain drain” effect may occur, similar to the academic fallout of the Soviet Union’s collapse in the 1990s. How Russia will participate in pre-war international research collaborations is still unknown. For now, a number of pre-war projects ranging from the Arctic to the fire-prone wilds of northern Russia are on hold. All of these scenarios paint a concerning picture about the progress of research. There are indications that Russian scientific collaboration may already be shifting eastward.
Philanthropic Impacts of War to Science
5. New Homes for Ukrainian Science
Finding support for Ukrainians emigrating from the conflict is difficult, but not impossible. Though many Ukrainians scientists remain in the country making the best of a difficult situation, approximately 6,000 are now living abroad. Most Ukrainian emigrants are now living in Poland and Germany. Some scientists continue to work remotely, supporting projects at their home institutions or with new research programs they’ve found since relocating. These success stories are thanks to the work of a number of ad-hoc mobilizations that help keep researchers working in the European cooperation. Groups like MSC4Ukraine help postdoc students and researchers find new opportunities across Europe. Social media trends like #Science4Ukraine help connect researchers to other supportive movements.
6. The International Rebuilding of Ukrainian Science
Various research institutions have also lent support to the survival and rebuilding of science in Ukraine:
The largest science prize, the Breakthrough Prize, recently donated $3 million to fund research programs and reconstruction efforts Federal research councils, like those in Netherlands and Switzerland, also have programs to formally support displaced scientists and researchers The European Union is investigating new funding schemes that could repurpose almost €320 billion of frozen Russian Federal Reserves
No Consensus on Boycott
While the Western front seems united in it’s condemnation of the war, the international science community isn’t in total agreement with a science boycott. Some scientists argue that excluding Russian scientists—especially those who have vocalized their disdain for the war—serves to punish unrelated individuals. This fractures the benefits of international scientific exchange. Others, especially those in countries who are economically dependent on Russia, have remained silent or even supported the invasion. In these cases, Russia’s science initiatives may lean more heavily in their direction. It’s easy to appreciate how war complicates many different angles of the global research ecosystem. After one year, how things will turn out remains a mystery. But one thing is for certain: science adapts and progresses even in the bleakest times. For now, supporting all efforts to reduce conflict remains in science’s best interests. Full sources here