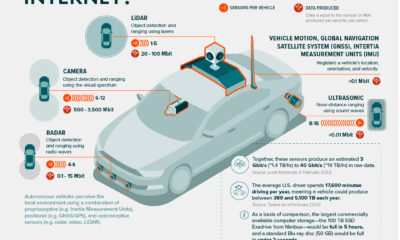
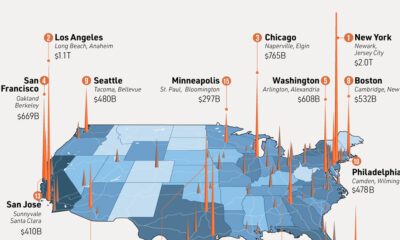
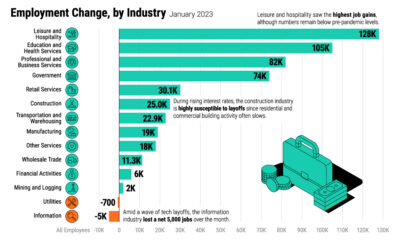
As autonomous vehicles become more of a looming certainty, what will be the wider impacts of this monumental transition?
Which Countries are Ready?
Today’s interactive visual from Aquinov Mathappan ranks countries on their preparedness to adopt self-driving cars, while also exploring the range of challenges they will face in achieving complete automation.
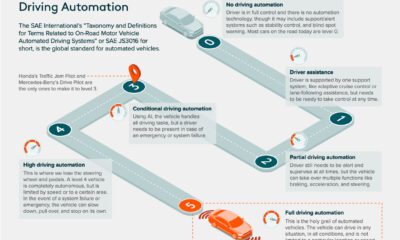
The Five Levels of Automation
The graphic above uses the Autonomous Vehicles Readiness Index, which details the five levels of automation. Level 0 vehicles place the responsibility for all menial tasks with the driver, including steering, braking, and acceleration. In contrast, level 5 vehicles demand nothing of the driver and can operate entirely without their presence. Today, most cars sit between levels 1 and 3, typically with few or limited automated functions. There are some exceptions to the rule, such as certain Tesla models and Google’s Waymo. Both feature a full range of self-driving capabilities—enabling the car to steer, accelerate and brake on behalf of the driver.
The Journey to Personal Driving Freedom
There are three main challenges that come with achieving a fully-automated level 5 status:
Which Countries are Leading the Charge?
The 20 countries were selected for the report based on economic size, and their automation progress was ranked using four key metrics: technology and innovation, infrastructure, policy and legislation, and consumer acceptance. The United States leads the way on technology and innovation, with 163 company headquarters, and more than 50% of cities currently preparing their streets for self-driving vehicles. The Netherlands and Singapore rank in the top three for infrastructure, legislation, and consumer acceptance. Singapore is currently testing a fleet of autonomous buses created by Volvo, which will join the existing public transit fleet in 2022. India, Mexico, and Russia lag behind on all fronts—despite enthusiasm for self-driving cars, these countries require legislative changes and improvements in the existing quality of roads. Mexico also lacks industrial activity and clear regulations around autonomous vehicles, but close proximity to the U.S. has already garnered interest from companies like Intel for manufacturing autonomous vehicles south of the border.
How Autonomous Vehicles Impact the Economy
Once successfully adopted, autonomous vehicles will save the U.S. economy $1.3 trillion per year, which will come from a variety of sources including:
$563 billion: Reduction in accidents $422 billion: Productivity gains $158 billion: Decline in fuel costs $138 billion: Fuel savings from congestion avoidance $11 billion: Improved traffic flow and reduction of energy use With the adoption of autonomous vehicles projected to reduce private car ownership in the U.S. to 43% by 2030, it’s disrupting many other industries in the process. Insurance Transportation will be safer, potentially reducing the number of accidents over time. Insurance companies are already rolling out usage-based insurance policies (UBIs), which charge customers based on how many miles they drive and how safe their driving habits are. Travel Long distance traveling in autonomous vehicles provides a painless alternative to train and air travel. The vehicles are designed for comfort, making it possible to sleep overnight easily—which could also impact the hotel industry significantly. Real Estate An increase in effortless travel could lead to increased urban sprawl, as people prioritize the convenience of proximity to city centers less and less. Defining the parameters for this emerging industry will present significant and unpredictable challenges. Once the initial barriers are eliminated and the technology matures, the world could see a new renaissance of mobility, and the disruption of dozens of other industries as a result.
Insurance Transportation will be safer, potentially reducing the number of accidents over time. Insurance companies are already rolling out usage-based insurance policies (UBIs), which charge customers based on how many miles they drive and how safe their driving habits are. Travel Long distance traveling in autonomous vehicles provides a painless alternative to train and air travel. The vehicles are designed for comfort, making it possible to sleep overnight easily—which could also impact the hotel industry significantly. Real Estate An increase in effortless travel could lead to increased urban sprawl, as people prioritize the convenience of proximity to city centers less and less. Defining the parameters for this emerging industry will present significant and unpredictable challenges. Once the initial barriers are eliminated and the technology matures, the world could see a new renaissance of mobility, and the disruption of dozens of other industries as a result.
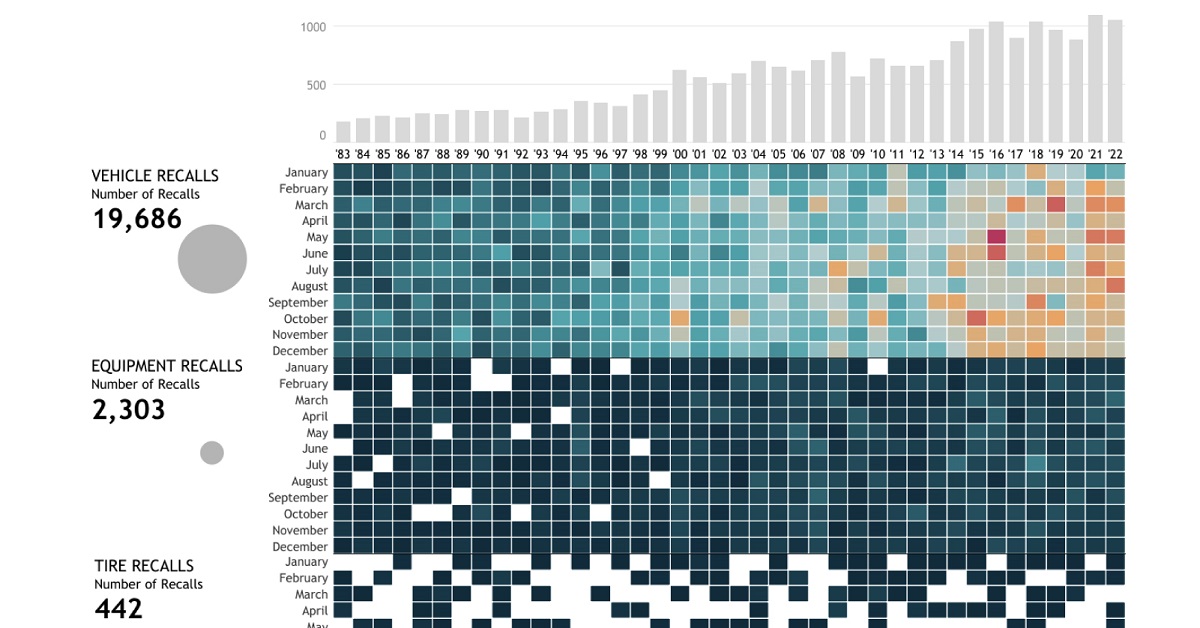
on These faulty airbags, installed by 19 different automakers including BMW and Toyota from 2002 to 2015, can explode when deployed and have led to numerous tragic accidents. Their recall affected 67 million airbags (including Honda’s vehicles above) and has been known as the largest safety recall in U.S. history. Over the past four decades, there have been over 22,000 automobile recalls in the United States. In this interactive piece, Chimdi Nwosu uses data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration to visualize the types of automobile recalls over the past 40 years, the companies with the most recalls, the components that were recalled the most, and, most importantly, their impacts on people.
Breaking Down U.S. Automobile Recalls
Whether a recall affects specific vehicle components, equipment, or vehicles as a whole, it affects the lives of millions of automobile users. When combined, these numbers ramp up exponentially. The U.S. alone has seen a total of 22,651 recalls over the past 40 years, impacting more than one billion people. Almost 72% of these people were affected by nearly 20,000 vehicle recalls, while around 19% were impacted by over 2,000 equipment recalls during this period. Comparatively, the 442 tire recalls and 220 child seat recalls affected significantly less, but still a total of 96.9 million people. While an inconvenience to many, the recall of these faulty vehicle parts saves many more from unfortunate incidents that may have occurred if left unchecked.
Minor and Major Recalls
One of the largest recalls in history took place in 2014 when General Motors—the manufacturer with the highest total of recalls in four decades—recalled millions of vehicles including the 2005-2007 Chevrolet Cobalt, 2007 Pontiac G5, and 2006-2007 Chevrolet HHR, amongst others. The reason for this recall was a faulty ignition switch that caused the vehicle’s engine to shut down while driving, disabling safety systems including airbags. This fault led to the death of hundreds of people. However, not all recalls are this severe. BMW, for example, recalled just four vehicles in December last year because one of the four bolts in the driver’s backrest was not attached properly. Similarly in 2020, Ford recalled some of its vehicles due to a faulty door latch. While this recall inconvenienced over two million users, it was less likely to lead to severe consequences if left unchecked.
A Safer Future?
The number of automobile recalls over the past four decades has seen a steep rise. As have car safety standards. While recalls could hint at the risks involved in taking your car out for a drive, they also indicate manufacturers taking responsibility for their faulty commodities, and affect a very small percentage of vehicles on the road. To improve automobile safety, the NHTSA proposed a New Car Assessment Program in 2022, which provides vehicle users with safety ratings for every new vehicle. This five-star safety rating program rates the vehicles’ safety features, crashworthiness, and resistance to rollover. With self-driving cars now also entering the mix, we need to stay informed about vehicle safety to keep our vehicles, our streets, and ourselves safe in the future.