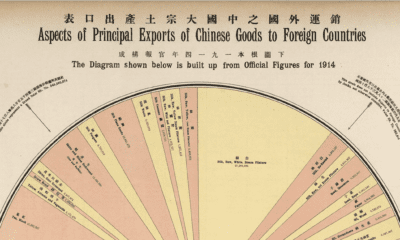
Most of that population growth will be concentrated in cities across Africa and Asia. To help paint a detailed picture, this map uses data from the United Nations to rank the top 20 fastest growing cities in the world in terms of average annual growth rate from 2020 to 2025.
Full Speed Ahead
The majority of the world’s fastest growing cities are located in Africa—in fact, 17 of the 20 are located on the continent, with four of the 20 cities being located in Nigeria specifically. Population growth is booming across the entire continent, as many countries retain high birth rates. According to the World Bank, the 2019 fertility rate (births per woman) in Sub-Saharan Africa was 4.6, compared to the global fertility rate of 2.4. Nigeria’s economy is largely based on petroleum which has resulted in the country becoming one of the strongest economies in Africa. This, coupled with a high birth rate and a resulting young population, has given the country a strong and rising workforce. However, the population growth in Nigeria is both a blessing and a curse. The success of the economy, among other factors, has resulted in excessive rural-to-urban migration. This mass exodus from rural areas has led to less farming, which means the country now needs to import basic food staples at a high cost. In Mozambique, Tete and Quelimane are growing 5.56% and 5.14% respectively. The country is expected to experience strong economic growth after facing contractions due to the pandemic. Forecasts predict that the Mozambiques’s economy will grow 4% by 2022.
Implications of Fast Growth
All of the top 20 fastest growing cities are located in either Africa or Asia, and they are far outpacing growth on other continents, such as Europe, for example. Fastest Growing Cities: Europe vs. Global By 2050, Sub-Saharan Africa will be home to close to 2 billion people and roughly half will be under the age of 25. This represents an enormous labor force and opportunities for innovation and growth. In fact, in navigating the pandemic, Africa is already starting to capitalize on digital advances in both traditional and new sectors. China has its eye on Africa, as evidenced through their multiple investments in infrastructure projects in the continent. Additionally, NATO countries have recently committed to investing similar amounts in Africa to counter China’s influence. In spite of the economic potential, increased city sizes could be problematic for some of these countries. They will need to adapt to the issues associated with mass urbanization, like pollution, overcrowding, and high costs of living.
Changing Tides
Population booms can lead to massive economic growth, a larger (and younger) working population, and a growing domestic consumer market. As the aforementioned cities continue their rapid expansion, and as people continue to flock to growing megacities in Africa and Asia, it could represent the beginning of an important economic shift that is worth keeping an eye on. on Cities become “expensive” due to a variety of factors such as high demand for housing, a concentration of high-paying businesses and industries, and a high standard of living. Additionally, factors such as taxes, transportation costs, and availability of goods and services can also contribute to the overall cost of living in global cities. The infographic above uses data from EIU to rank the world most and least expensive cities to live in. To make the list, the EIU examines 400+ prices for over 200 products and services in 172 cities, surveying a variety of businesses to track price fluctuations over the last year.
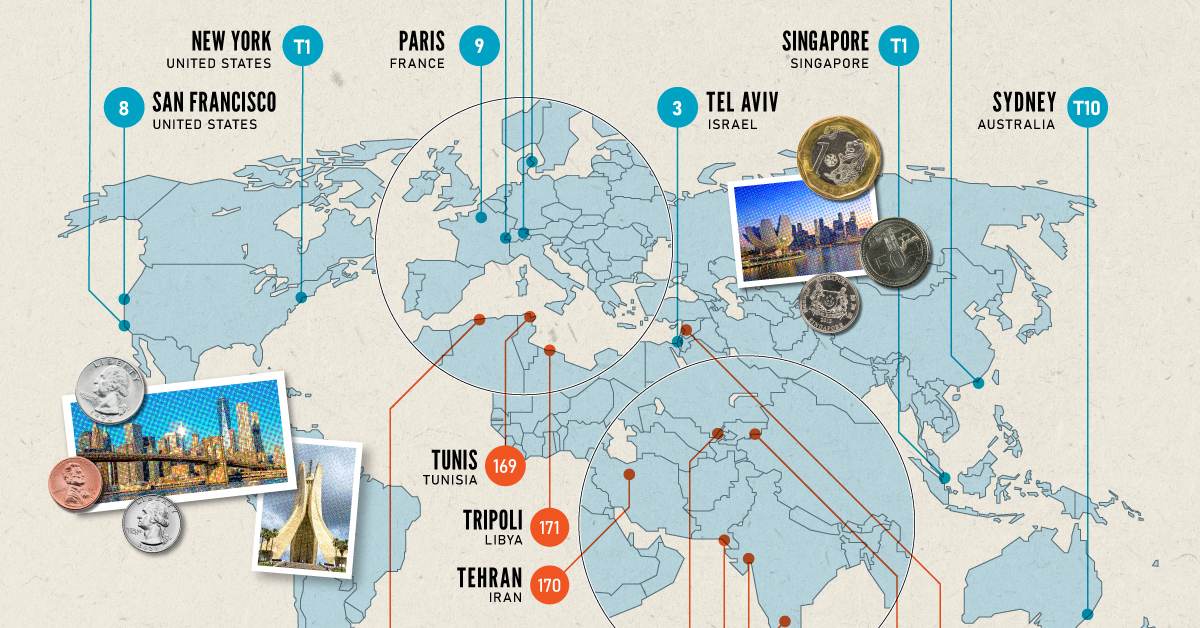
Inflation + Strong Currency = Expensive Cities
If you live in a city where many residents find it challenging to put a roof over their heads, food on their plates, and make ends meet, you live in an expensive city. But if this inflation is compounded with a strong national currency, you may live in one of the world’s most expensive cities. Singapore and New York City tied for the first rank amongst the world’s most expensive cities in 2022, pushing Israel’s Tel Aviv from the first place in 2021 to the third place in 2022. Both these cities had high inflation and a strong currency. Surprisingly, this is the Big Apple’s first time atop the ranking. The city with one of the most expensive real estate markets worldwide, Hong Kong ranked fourth in this list, followed by Los Angeles, which moved up from its ninth rank in 2021.
Poor Economies = Cheaper Cities
Asia continues to dominate the list of the world’s least expensive cities, followed by parts of North Africa and the Middle East. Though affordability sounds good at face value, sitting at the bottom of the ranking isn’t necessarily a coveted position. While the cost of living in some of the cities in these nations is low, it comes at the price of a weak currency, poor economy, and, in many cases, political and economic turmoil. The decade-long conflict in Syria weakened the Syrian pound, led to a spiraling inflation and fuel shortages, and further collapsed its economy. It’s no surprise that its capital city of Damascus has maintained its position as the world’s cheapest city. Tripoli and Tehran, the capitals of Libya and Iran, respectively, follow next on this list, reflecting their weakened economies. Meanwhile, seven cities in Asia with the common denominator of high-income inequality and low wages dominate the list of the world’s cheapest cities. These include three Indian cities, Tashkent in Uzbekistan, Almaty in Kazakhstan, Pakistan’s most populous city of Karachi, and Sri Lankan capital–Colombo.