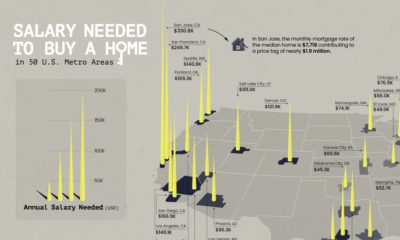
However, as UBS notes in its latest report, there is also growing concern about another prominent bubble that’s been in the works since the aftermath of the financial crisis. Large amounts of easy money have fueled real estate bubbles in the world’s major cities – and the Swiss investment bank now sees the property markets in six global cities as being at risk.
The Bubble Index
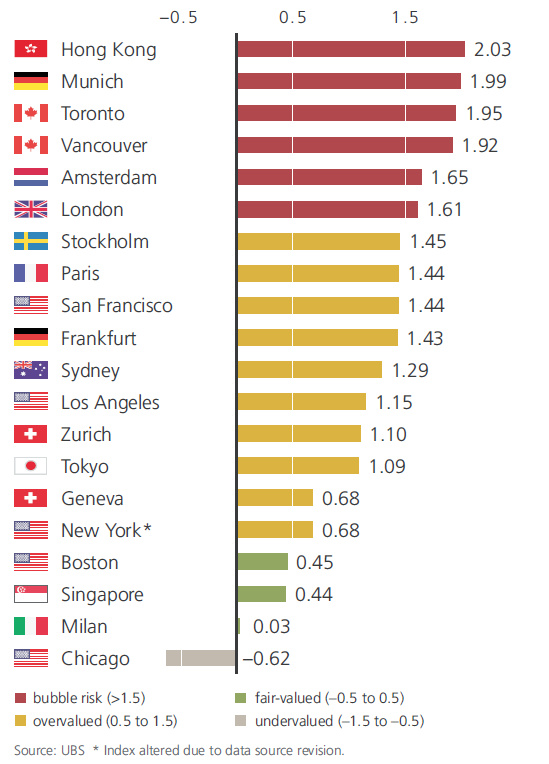
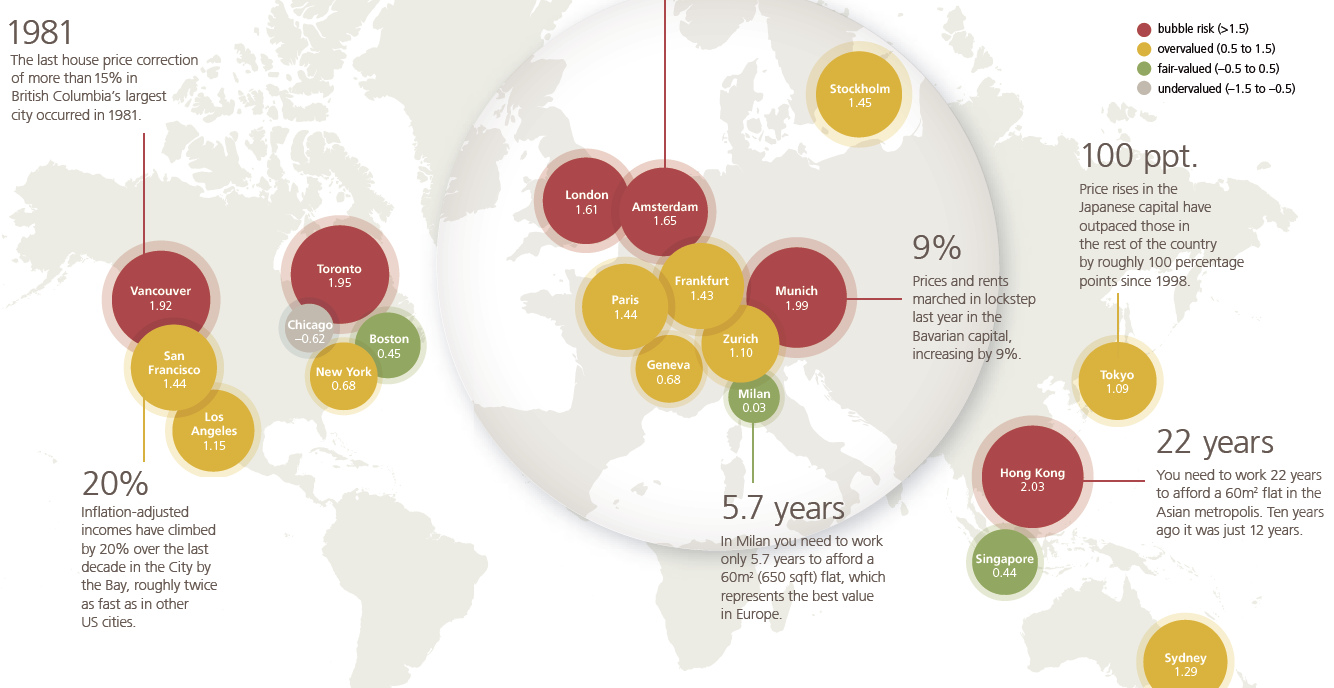
In the 2018 edition of the bank’s Real Estate Bubble Index, here are the major cities around the globe that are in or near bubble territory:
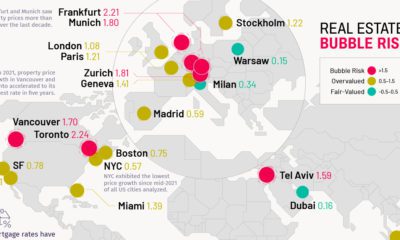
Any city with a score over 1.5 is considered at “Bubble Risk”, and right now those include two cities from Canada, one from Asia, and three from Europe. Hong Kong (2.03) tops the index this year, leaping past Munich (1.99), Toronto (1.95), and Vancouver (1.92) which all remain at bubble risk themselves. Amsterdam and London are the two other cities that score higher than a 1.5 on the rankings. It’s also very important to note that there are four cities that score just under the 1.5 threshold: Stockholm (1.45), Paris (1.44), San Francisco (1.44), and Frankfurt (1.43).
A Coming Correction?
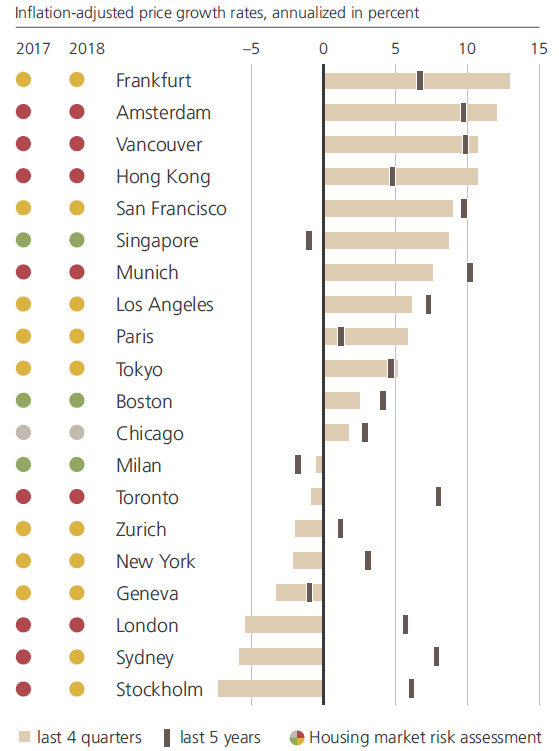
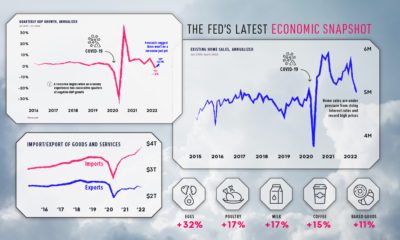
Investor and writer Howard Marks has noted in recent months that the wider market is in its “8th inning”, and the same case could be made for real estate. – UBS Report According to UBS, the cracks are already starting to show at the top end of the market, with housing prices declining in half of last year’s list of bubble cities. Some of the worrying factors include rising interest rates, as well as growing political tensions as the crisis of affordability makes it harder for average people to live in these global financial centers. Here is annualized growth in percent over the last year, as well for the last five years for cities in the index:
As you can see, some of these cities have had negative growth over the last 12 months, including New York, Toronto, Sydney, London, and Stockholm.
Charting Specific Markets
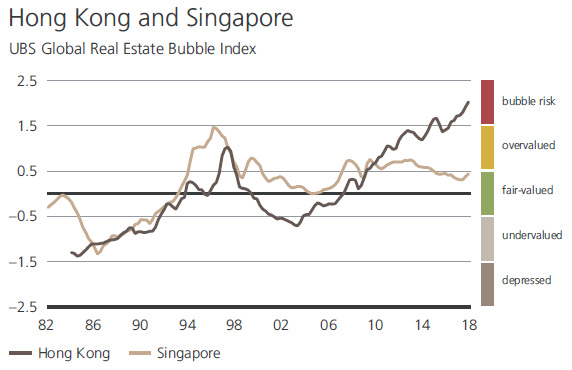
In Hong Kong, you need to work 22 years to afford a 645 sq. ft (60m²) apartment, when that took just 12 years just a decade ago. In recent years, Hong Kong’s ascent to becoming one of the biggest real estate bubbles has become very evident, especially when juxtaposed with Singapore:
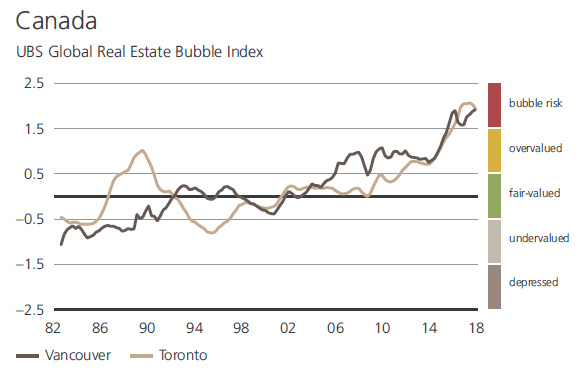
In Canada, the two cities in the index are starting to go in alternate directions, although recent signs also point to a potential slowdown in Vancouver:
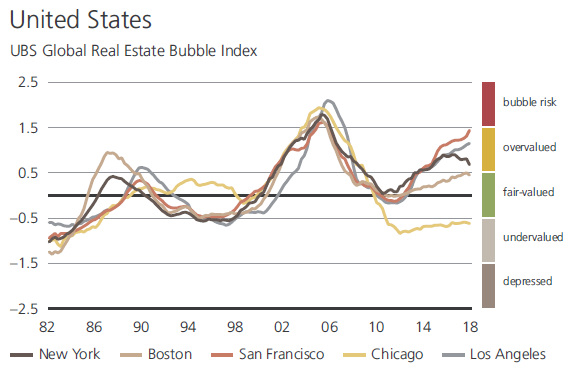
Finally, the U.S. market – which felt the pain of the housing crash in the late 2000s – is home to zero cities in the bubble risk category, according to UBS.
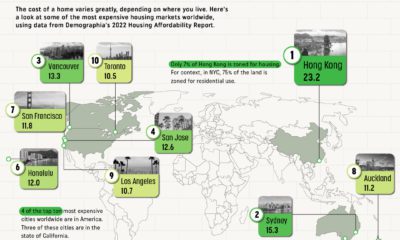
Whether it is a bubble or not, many people agree that San Francisco’s housing situation is still a crisis. In the Bay Area hub, 60% of all rental units are in rental-controlled buildings, and the median single-family house price is a hefty $1.7 million. on Cities become “expensive” due to a variety of factors such as high demand for housing, a concentration of high-paying businesses and industries, and a high standard of living. Additionally, factors such as taxes, transportation costs, and availability of goods and services can also contribute to the overall cost of living in global cities. The infographic above uses data from EIU to rank the world most and least expensive cities to live in. To make the list, the EIU examines 400+ prices for over 200 products and services in 172 cities, surveying a variety of businesses to track price fluctuations over the last year.
Inflation + Strong Currency = Expensive Cities
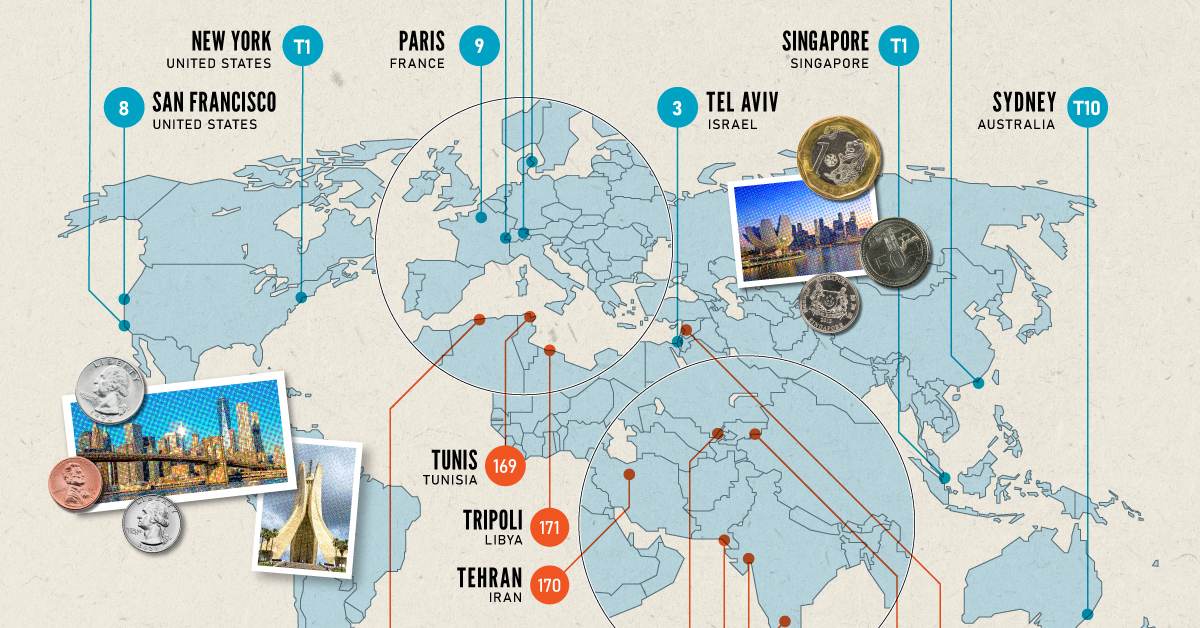
If you live in a city where many residents find it challenging to put a roof over their heads, food on their plates, and make ends meet, you live in an expensive city. But if this inflation is compounded with a strong national currency, you may live in one of the world’s most expensive cities. Singapore and New York City tied for the first rank amongst the world’s most expensive cities in 2022, pushing Israel’s Tel Aviv from the first place in 2021 to the third place in 2022. Both these cities had high inflation and a strong currency. Surprisingly, this is the Big Apple’s first time atop the ranking. The city with one of the most expensive real estate markets worldwide, Hong Kong ranked fourth in this list, followed by Los Angeles, which moved up from its ninth rank in 2021.
Poor Economies = Cheaper Cities
Asia continues to dominate the list of the world’s least expensive cities, followed by parts of North Africa and the Middle East. Though affordability sounds good at face value, sitting at the bottom of the ranking isn’t necessarily a coveted position. While the cost of living in some of the cities in these nations is low, it comes at the price of a weak currency, poor economy, and, in many cases, political and economic turmoil. The decade-long conflict in Syria weakened the Syrian pound, led to a spiraling inflation and fuel shortages, and further collapsed its economy. It’s no surprise that its capital city of Damascus has maintained its position as the world’s cheapest city. Tripoli and Tehran, the capitals of Libya and Iran, respectively, follow next on this list, reflecting their weakened economies. Meanwhile, seven cities in Asia with the common denominator of high-income inequality and low wages dominate the list of the world’s cheapest cities. These include three Indian cities, Tashkent in Uzbekistan, Almaty in Kazakhstan, Pakistan’s most populous city of Karachi, and Sri Lankan capital–Colombo.