The U.S. aims to cut its greenhouse gas emissions in half by 2030 as part of its commitment to tackling climate change, but might be lacking the critical minerals needed to achieve its goals. The American green economy will rely on renewable sources of energy like wind and solar, along with the electrification of transportation. However, local production of the raw materials necessary to produce these technologies, including solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicles, is lacking. Understandably, this has raised concerns in Washington. In this graphic, based on data from the U.S. Geological Survey, we list all of the minerals that the government has deemed critical to both the economic and national security of the United States.
What are Critical Minerals?
A critical mineral is defined as a non-fuel material considered vital for the economic well-being of the world’s major and emerging economies, whose supply may be at risk. This can be due to geological scarcity, geopolitical issues, trade policy, or other factors. In 2018, the U.S. Department of the Interior released a list of 35 critical minerals. The new list, released in February 2022, contains 15 more commodities. Much of the increase in the new list is the result of splitting the rare earth elements and platinum group elements into individual entries rather than including them as “mineral groups.” In addition, the 2022 list of critical minerals adds nickel and zinc to the list while removing helium, potash, rhenium, and strontium. The challenge for the U.S. is that the local production of these raw materials is extremely limited. For instance, in 2021 there was only one operating nickel mine in the country, the Eagle mine in Michigan. The facility ships its concentrates abroad for refining and is scheduled to close in 2025. Likewise, the country only hosted one lithium mine, the Silver Peak Mine in Nevada. At the same time, most of the country’s supply of critical minerals depends on countries that have historically competed with America.
China’s Dominance in Minerals
Perhaps unsurprisingly, China is the single largest supply source of mineral commodities for the United States. Cesium, a critical metal used in a wide range of manufacturing, is one example. There are only three pegmatite mines in the world that can produce cesium, and all were controlled by Chinese companies in 2021. Furthermore, China refines nearly 90% of the world’s rare earths. Despite the name, these elements are abundant on the Earth’s crust and make up the majority of listed critical minerals. They are essential for a variety of products like EVs, advanced ceramics, computers, smartphones, wind turbines, monitors, and fiber optics. After China, the next largest source of mineral commodities to the United States has been Canada, which provided the United States with 16 different elements in 2021.
The Rising Demand for Critical Minerals
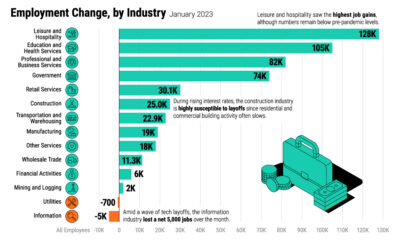
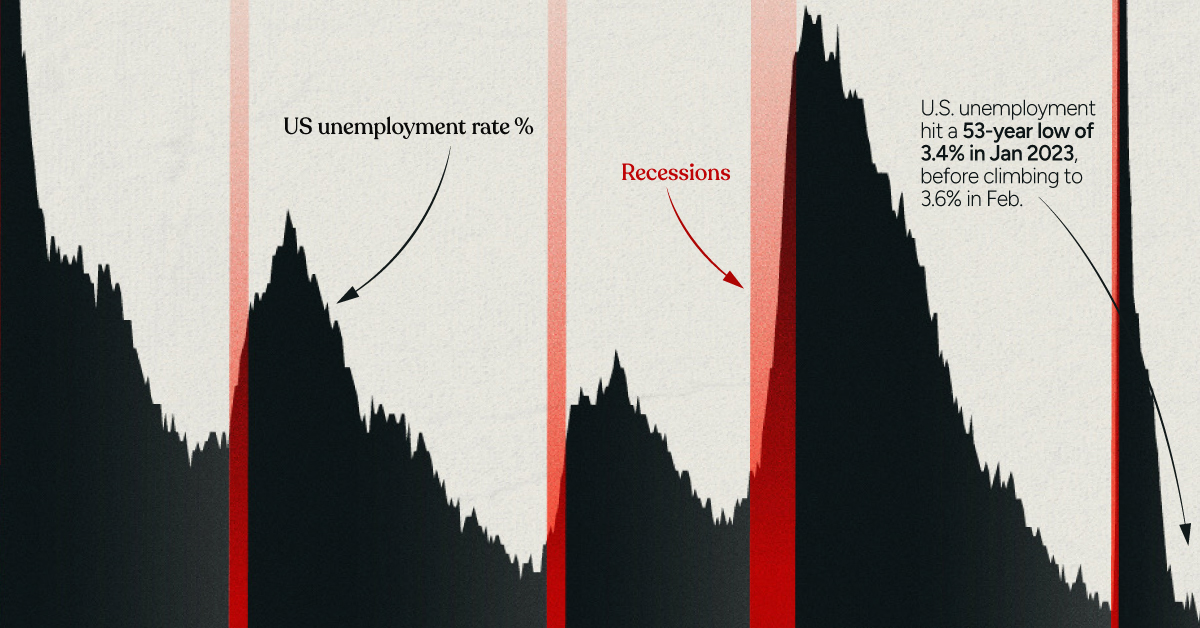
As the world’s clean energy transitions gather pace, demand for critical minerals is expected to grow quickly. According to the International Energy Association, the rise of low-carbon power generation is projected to triple mineral demand from this sector by 2040. The shift to a sustainable economy is important, and consequently, securing the critical minerals necessary for it is just as vital. on Both figures surpassed analyst expectations by a wide margin, and in January, the unemployment rate hit a 53-year low of 3.4%. With the recent release of February’s numbers, unemployment is now reported at a slightly higher 3.6%. A low unemployment rate is a classic sign of a strong economy. However, as this visualization shows, unemployment often reaches a cyclical low point right before a recession materializes.
Reasons for the Trend
In an interview regarding the January jobs data, U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen made a bold statement: While there’s nothing wrong with this assessment, the trend we’ve highlighted suggests that Yellen may need to backtrack in the near future. So why do recessions tend to begin after unemployment bottoms out?
The Economic Cycle
The economic cycle refers to the economy’s natural tendency to fluctuate between periods of growth and recession. This can be thought of similarly to the four seasons in a year. An economy expands (spring), reaches a peak (summer), begins to contract (fall), then hits a trough (winter). With this in mind, it’s reasonable to assume that a cyclical low in the unemployment rate (peak employment) is simply a sign that the economy has reached a high point.
Monetary Policy
During periods of low unemployment, employers may have a harder time finding workers. This forces them to offer higher wages, which can contribute to inflation. For context, consider the labor shortage that emerged following the COVID-19 pandemic. We can see that U.S. wage growth (represented by a three-month moving average) has climbed substantially, and has held above 6% since March 2022. The Federal Reserve, whose mandate is to ensure price stability, will take measures to prevent inflation from climbing too far. In practice, this involves raising interest rates, which makes borrowing more expensive and dampens economic activity. Companies are less likely to expand, reducing investment and cutting jobs. Consumers, on the other hand, reduce the amount of large purchases they make. Because of these reactions, some believe that aggressive rate hikes by the Fed can either cause a recession, or make them worse. This is supported by recent research, which found that since 1950, central banks have been unable to slow inflation without a recession occurring shortly after.
Politicians Clash With Economists
The Fed has raised interest rates at an unprecedented pace since March 2022 to combat high inflation. More recently, Fed Chairman Jerome Powell warned that interest rates could be raised even higher than originally expected if inflation continues above target. Senator Elizabeth Warren expressed concern that this would cost Americans their jobs, and ultimately, cause a recession. Powell remains committed to bringing down inflation, but with the recent failures of Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank, some analysts believe there could be a pause coming in interest rate hikes. Editor’s note: just after publication of this article, it was confirmed that U.S. interest rates were hiked by 25 basis points (bps) by the Federal Reserve.